An event of the OCS Soft team's special project - "PROdemo: Software Solutions Laboratory." Participants include Alexander Kalinin, presale specialist for backup at OCS, and Alexander Savostyanov, technical expert at OCS, who will provide an overview of the architecture, discuss product use cases, and demonstrate the main elements of the management interface, the operation of the software-defined data storage, and the virtualization subsystem.

Today they will be talking about cyber infrastructure. Have we recently updated our corporate design? In addition, we have updated our demo site. Here you can see the demo stands that we have in various areas. All of them are implemented on the basis of our data center.

Three sites, 65 servers, 14 TB of RAM, and decent networks, working normal storage systems, we have graphics cards. And we provide remote access to these stands via VDI technology.

For our partners, we provide a range of activities such as technical requirements analysis, solution demonstrations, solution selection, pilots, and implementation. We conduct various seminars, training courses, and webinars. Here are stands for self-study. Sometimes we prepare individual stands according to customer requirements and provide demo equipment.
Two large sections are virtualization and information security. And there are a large number of different platforms here. The main thing is that on this stand you can click the "More Details" button, view some screenshots from the management console, see what demonstration scenarios are available, what the stand consists of, and you can also click the "Book" button. Your request will come to us in Telegram, and we will definitely contact you and clarify what exactly you want to test, what deadlines suit you, etc.
Then Alexander Savostyanov took the floor. He first gave a short presentation about the product.

Cyber infrastructure is an infrastructure in which the computing resources of servers and storage devices are combined at the software level. With this method of presentation, only standard architecture servers are used as the hardware platform, which allows you to create an infrastructure of any scale to solve a larger number of IT tasks.
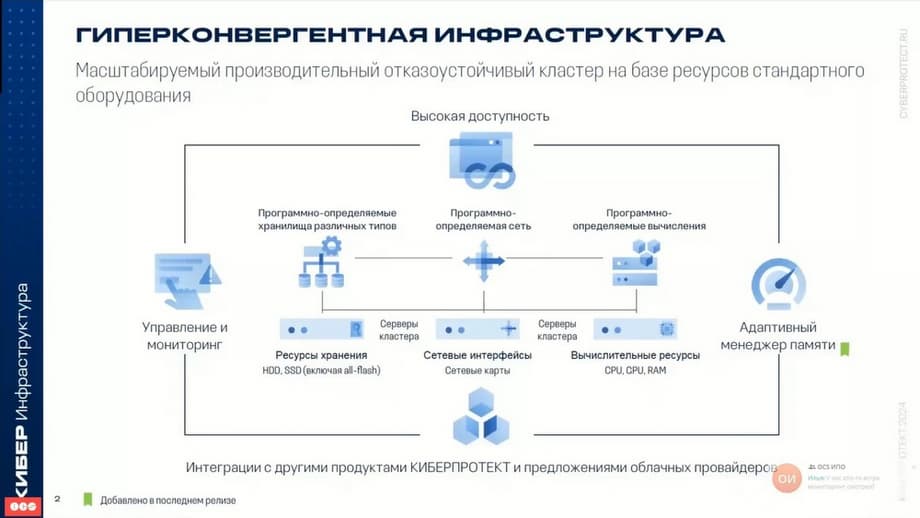
The cyber infrastructure is based on a very simple idea. Servers are taken, they can be from different manufacturers and different configurations. These servers are connected by network interfaces, connected to the external and internal networks. The internal network is used for communication between nodes and for cluster interconnect, and is used for data storage. Software is installed on the "bare metal" that combines these servers into a reliable, high-performance, fault-tolerant cluster. All the resources of these servers - computing power, memory, and storage - are combined into a single pool. The cyber infrastructure is based on the Linux operating system. The distribution includes the operating system, although there are options when you can install the operating system separately, and the cyber infrastructure software itself can be installed on top of the operating system. However, most often all this is installed at the same time. A single cluster of combined servers is easily scaled by adding nodes and individual disks.
On the slide, we see that the cyber infrastructure includes software-defined storage of various types, software-defined network, and software-defined computing. All this is managed from a web interface, from the command line, and there are management and monitoring systems.
The main component and what this product started with a long time ago is software-defined storage.
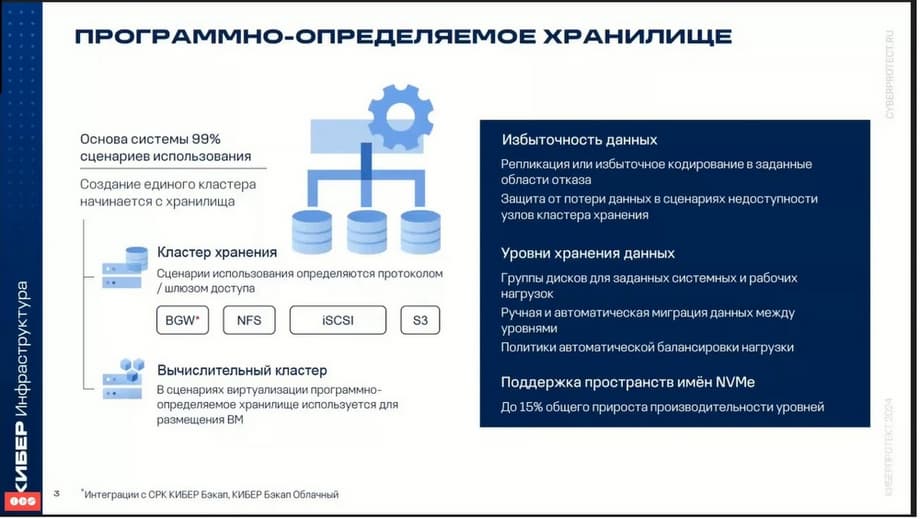
Cyber infrastructure allows you to create various types of storage with access via NFS, iSCSI, and S3 protocols. Also, additionally for integration with other Cyberprotect products, backup products such as CYBER Backup Cloud and Cyber Backup, a special storage is also used, which is designated by the abbreviation BGW (Backup Gateway). Thus, various types of storage are supported. S3 storage for storing an unlimited number of objects and files, although there are certain limitations, although they are a bit marketing-oriented. Also, iSCSI block storage is used and recommended for virtualization of databases and other workloads. As already mentioned, additional storage can also be used as a Backup Gateway, which is designed for the backup system. The creation of file, block, and object storage systems is achieved by combining storage devices into a single pool. That is, the disk resources of each of the servers are added to this single pool and, thus, they are combined into a single storage.
One of the most popular types of storage now is object storage. Cyber infrastructure allows you to export the disk space of the cluster in the form of S3 compatible storage.
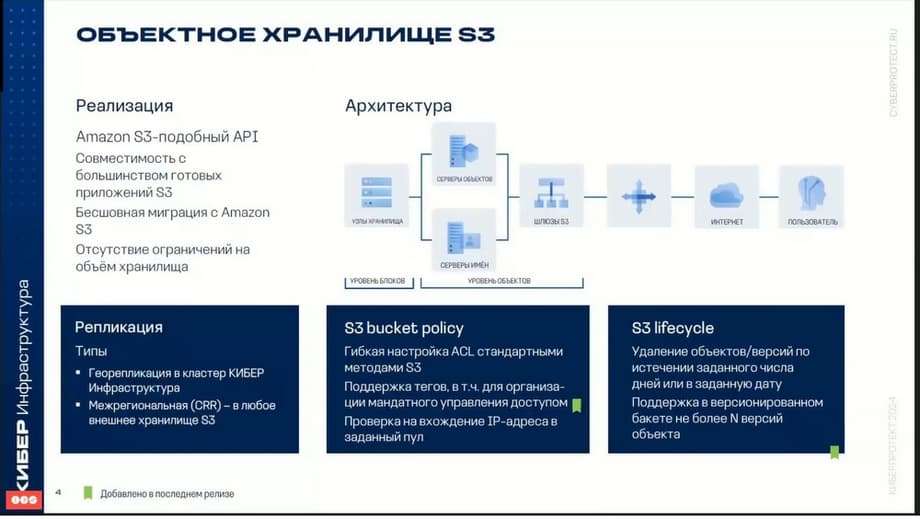
Object storage is optimized for storing billions of objects, data, and applications, you can store various static web content, online storage service data, big data, backups, etc. The key difference compared to other types of storage used in cyber infrastructure is that parts of an object cannot be changed. That is, when an object is changed, a new version of it is formed. Cyber infrastructure can store replicas of S3 cluster data and keep them up to date in multiple geographically distributed data centers. That is, there is the possibility of geo-replication from one storage to another. Thus, they can be used for disaster recovery of data.

Block and file storage. First of all, it makes sense to talk about iSCSI and NFS. These are the main additional systems of storage type. iSCSI is recommended for virtualization of databases and other workloads. For example, databases and transactional systems. Data exchange with the storage occurs quickly due to the provision of high read and write speeds. Additional tools such as RDMA, which works on top of InfiniBand, can be used to increase speed, but this is specifically to ensure high storage performance.
NFS file storage can be used to store any type of corporate data with access via NFS. The NFS storage itself is built on the basis of object storage and can be scaled to billions of entities. It has high performance, but for using storage where high I/O performance is required, it is recommended to use iSCSI, not NFS.
Another type of storage is the backup gateway. Cyber Backup and Cyber Backup Cloud backup systems, as part of backup and replication tasks, transfer backups to the gateway. Thus, the cyber infrastructure itself can be used as backup storage, or it can be used as a gateway in order to be able to use the gateway for storage inside the storage itself of the backup, or you can use the gateway as a kind of cache that will be used to transfer data further in the external storage system. This can be either S3 or NFS. How does it work? The gateway is used as a cache. Data first enters the gateway, and then it enters further into the external S3 or NFS storage.
Redundancy is used to protect data during storage. Two technologies are used. One technology is called replication, the other is redundant coding.
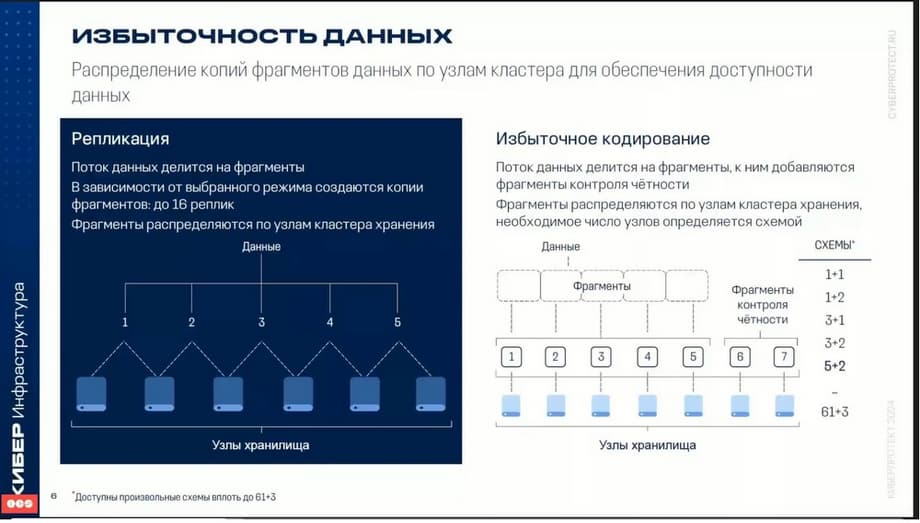
Replication is, in essence, data mirroring. Replication works as follows: the data stream is divided into separate blocks, each of which is stored in two or three places on other servers. Thus, there is data redundancy, either 100% or 200% data redundancy, but at the same time, maximum protection against failure is achieved. Redundant coding, or, in English, RG-coding, is a mechanism for dividing streams into separate blocks according to a certain redundancy scheme. Various schemes are used: 1+1, 1+2, 3+1, 3+2, 5+2,…, 61+3. Which scheme to use depends on the choice of various criteria. You can use with maximum reliability the failure of two or more nodes, or you can consider more high-performance schemes.
Areas of failure. High availability of systems is ensured through flexible settings, among which areas of failure can be distinguished.
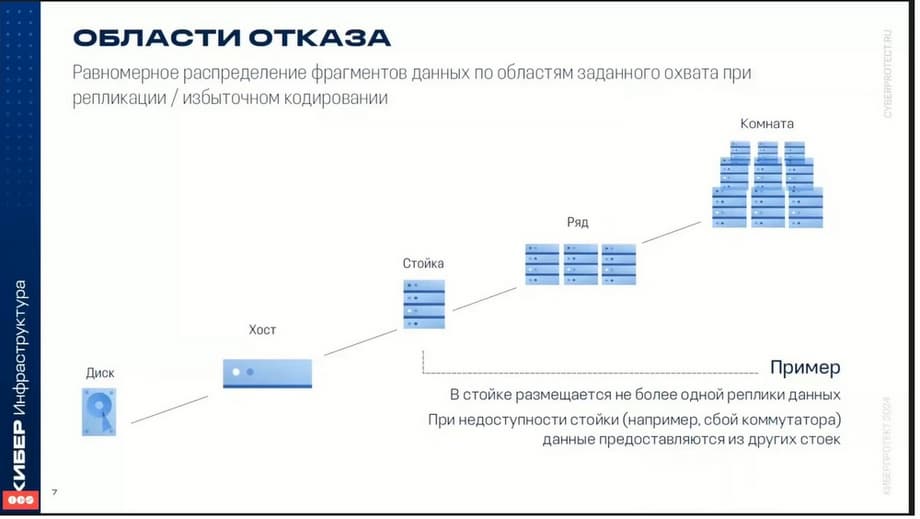
A disk, host, server, or even an entire rack can be selected as a failure zone. In this case, the data is distributed between separate components of the same level. That is, between disks, between servers, but most often this happens precisely between servers. I will show where the data is distributed between different servers. Thus, the failure of one or even two servers does not lead to data loss. If a component, for example, a server, fails, the data that was on this server is redistributed to other servers. That is, if there were any copies of data on the server that failed, then these copies of data will be distributed to other servers in such a way as to comply with the level of fault tolerance. That is, if the level of fault tolerance, for example, replicas, is two or three, then the data will be redistributed in such a way as to ensure the required level of data protection. Well, and, of course, it also depends on whether there is free space in the cluster.
Cyber infrastructure allows you to distribute data across multiple storage tiers and even automatically balance data. The meaning is that you can distribute different workloads across different storage tiers.
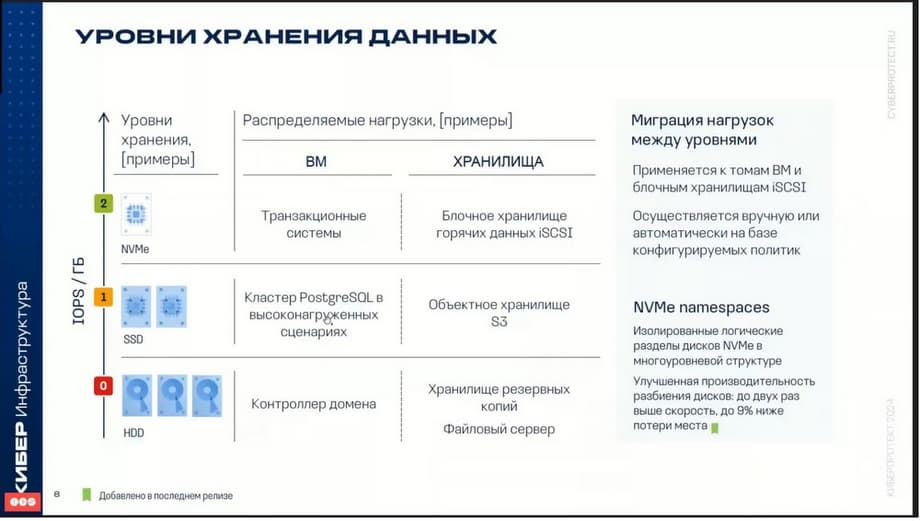
Let's say, here on the slide, you can see that transactional loads or hot data can be distributed to the level where NVMe drives are located. The next level is SSD drives. On it, for example, you can place database data or object storage data. In the third level - the slowest drives. At this level, you can store, for example, backups or some cold files.
Speaking of technical aspects during setup, you will encounter that different roles are assigned to the drives located on the server.

The first role of the system disk is needed to install the operating system and software. The second level is the metadata server. Metadata servers are responsible for data information about the cluster, track data fragments, status, etc. There must be more than one metadata server. Two or more servers are recommended. The third level is caching. Some disks can be assigned as a cache. For example, if we use regular HDD disks as the main storage disks, SSD can be used as a cache to increase performance. The last level is the fragment server, it acts as a storage.
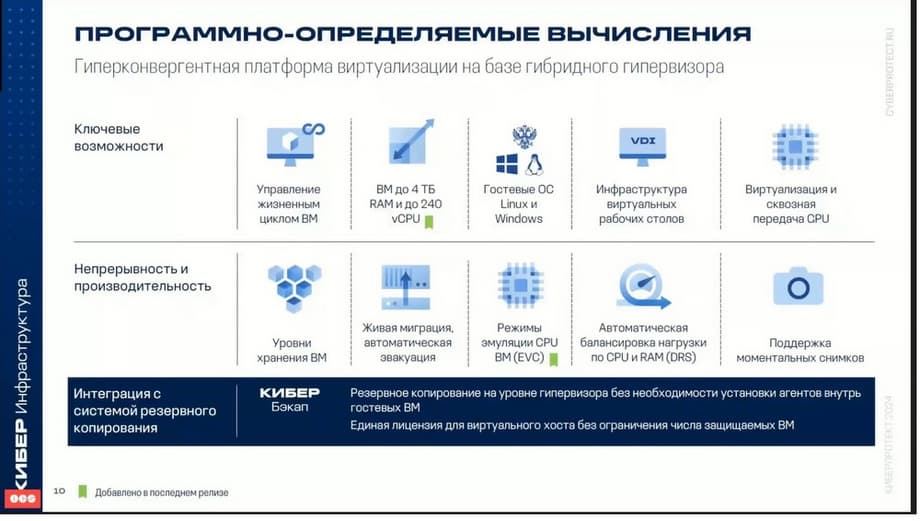
Now we move on to software-defined computing. The cyberinfrastructure includes a virtualization platform. That is, a virtualization platform can be deployed on top of the storage. OpenStack is used as a virtualization platform. And those who are familiar with the capabilities of OpenStack will immediately see that all the capabilities of this product are present. Storing virtual machines that are created as storage uses either the cyberinfrastructure storage itself or external storage.
Various operating systems of the Windows family, as well as the Linux family, can naturally act as guest operating systems. The product has all the basic properties and functions that a modern virtualization system should have. The entire life cycle of virtual machines is supported. That is, creating templates, turning on and off, transferring machines between nodes. The product implements all the basic functions, plus some additional features that not every virtualization system has. For example, you can set storage rules and storage policies for virtual machines. If a virtual machine requires high performance, it can be placed on a specific storage level that has higher I/O performance. And it is possible, and this can be set in the virtual machine settings, to ensure that in the future, when migrating between nodes, this virtual machine could be located on another level.
The virtualization system provides high availability of virtual machines. That is, if a server node on which a virtual machine was running fails, it can be evacuated to another node. There are modes of both cold migration and hot migration for transferring virtual machines between nodes. In one of the latest versions, DRS was introduced - this is the ability to balance load on CPU and memory. This feature allows you to automatically, without stopping, move virtual machines between virtualization servers to improve performance. This is also configurable. An administrator can, for example, exclude individual machines from this process or, conversely, include them.
The mechanism for creating snapshots is supported. It must be said that in the latest version a feature was also included to deploy virtualization of desktops, that is, VDI desktop infrastructure, on top of the virtualization system. These are the main features.
Regarding the placement of virtual machine disks.
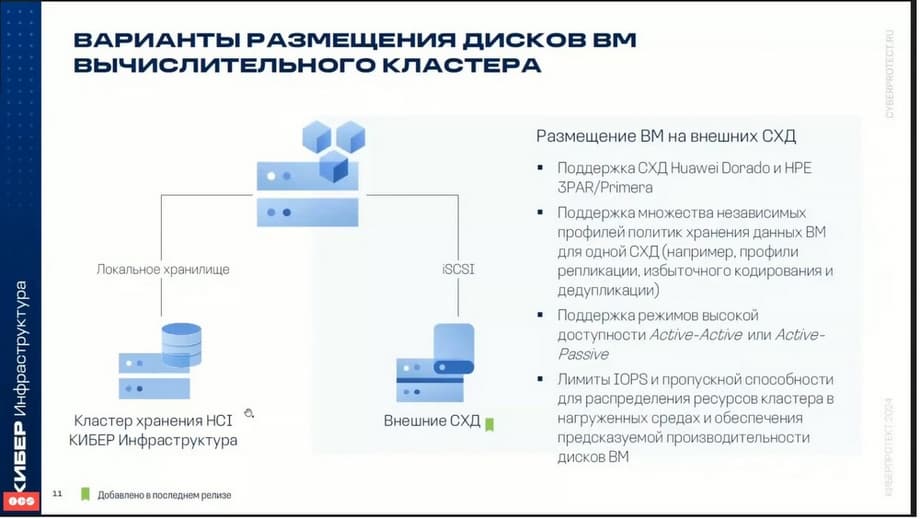
The simplest and most obvious is when virtual machine disks are stored in the same cyberinfrastructure storage. But you can also use external storage disks in it. This was added in the latest version. Currently, two storage systems are supported. These are Huawei Dorado and HPE 3PAR. It works the same way as in VMware. An analogue of what was called Vivo in VMware. That is, on the storage system, the cyberinfrastructure can create the necessary disks via the API and connect them to a virtual machine on external storage systems via the API. This is how it works.
In the near future, it is planned to support the Fibre Channel protocol. Currently, only iSCSI is supported, but this technology will be developed. Many customers are asking about this. Therefore, there will be the next version with support for the Fibre Channel protocol, so that you can externally connect from HD via the Fibre Channel interface.
Migration between platforms. Cyberinfrastructure migrates virtual machines from VMware, Hyper-V into cyberinfrastructure using a virtual appliance. The virtual appliance is called V2V appliance for transferring virtual machines. Migration of virtual machines from VMware is available in standalone and online modes. Migration of Hyper-V virtual machines is only available in standalone mode.

Software-defined network. As already mentioned, the virtualization system is based on the OpenStack product. Therefore, many things are known and understandable to those who are familiar with how OpenStack is structured.
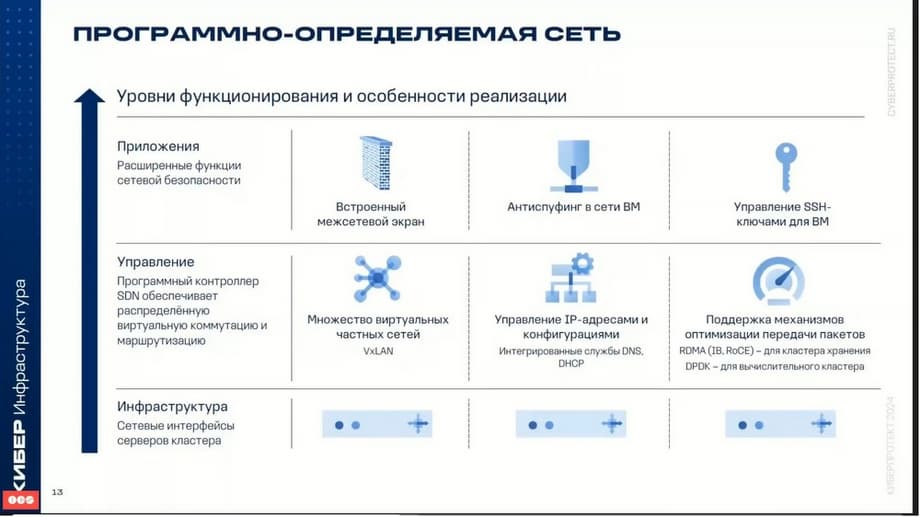
Cyberinfrastructure supports virtual switching based on OpenViSwitch. The OpenViSwitch switch runs on each compute node, redirects network traffic between virtual machines on this node, as well as between virtual machines and infrastructure networks, i.e. between other nodes. Distributed virtual switching provides centralized monitoring, configuration management on all nodes of the compute cluster. Distributed virtual routing allows you to place virtual routers on compute nodes and redirect virtual machine traffic directly from the placement nodes. In the scenario, the IP address is used directly, assigned to the network interface. If S is used, traffic is redirected through management nodes. As you know, the technology inside OpenStack, as in cyberinfrastructure, uses VxLAN technologies for virtual networks. This technology allows you to create logical L2 networks in L3 networks by encapsulating over UDP packets. There is also integration with DNS and DHCP services. You can use RDMA over InfiniBand for the storage cluster, to organize the internal storage network. The internal storage network is used to organize the storage. It can be built on the basis of RDMA.
Also as in OpenStack, it is possible to use a multi-tenant architecture in cyberinfrastructure, which is used in the construction of private and public clouds.
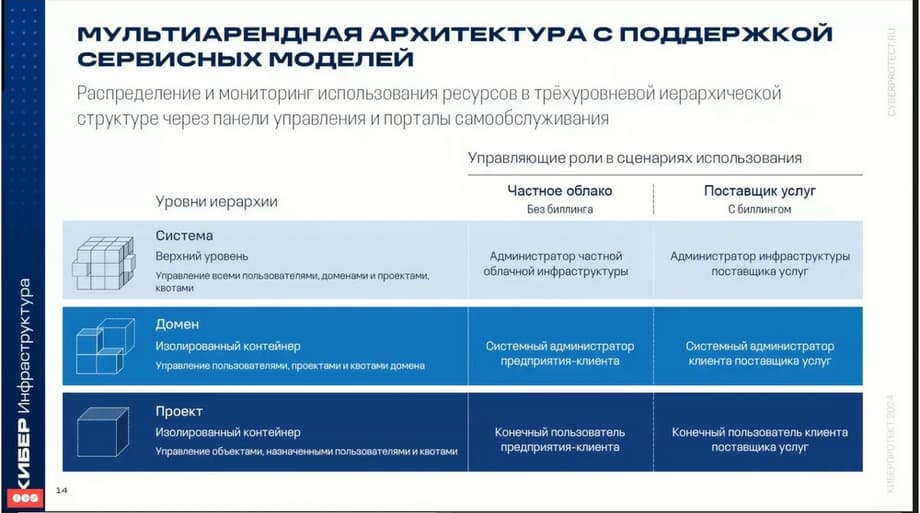
Cyberinfrastructure uses an administrative hierarchy of domains and projects. Projects are also called tenants with role-based access control for managing virtual objects of the compute cluster, such as virtual machines, volumes, virtual networks. A domain represents an isolated container of projects and users with assigned roles. Each project and user can belong to only one domain. A project is an isolated container of virtual objects with assigned users and specified restrictions for virtual resources, such as virtual central processors, RAM, storage and floating IP addresses.
In accordance with these levels, the product provides three user roles: system administrator, domain administrator and project participant.
Continuity of work. High availability ensures the operation of cyberinfrastructure services even in the event of a node failure.
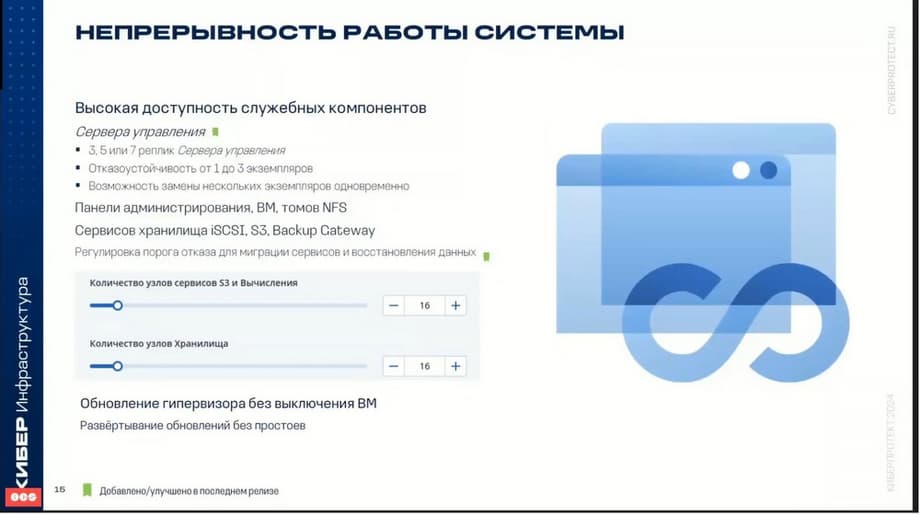
In the event of a failure of some node, the services that were running on this node are moved to healthy nodes in accordance with the RAFT consensus algorithm, which is used for fault tolerance in the system in the event of a failure. What methods are used to achieve high availability? First, it is metadata redundancy. For reliable operation, it is necessary to configure several metadata servers. In order for other nodes to pick up this work in the event of a failure of one. Data redundancy itself is the second method that is also used to ensure continuity and data protection.
Cyberinfrastructure provides high availability of all services. This refers to the administrator panel. The management server is usually clustered, and there are usually several management servers in the system.
Virtual machines. If a virtual machine fails, the cyberinfrastructure, the virtualization system itself, moves this machine to other free nodes. iSCSI services, I3, S3, Backup Gateway, NFS, all these services are protected from failure.
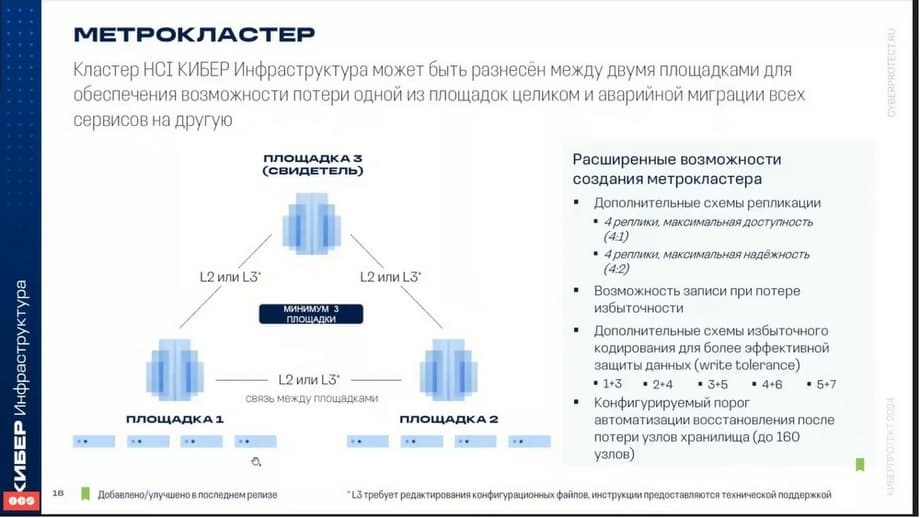
Metrocluster. In one of the latest versions, it became possible to build a metrocluster, i.e. to separate the cyberinfrastructure nodes between different sites to eliminate the possibility of losing the entire site.
Centralized management.

Infrastructure management is carried out in various ways. There is a main tool for this - a web interface, a command line, the so-called vinfra CLI interface, and also the OpenStack API, the OpenStack software interface. The Web console is the main visual interface for managing the computing cluster and storage cluster. Through the Web console, you can manage servers, networks, users, self-service, roles, security, etc.
The Vinfra command line interface is used to manage the storage cluster and computing cluster. It supports a unified syntax and various command formats.
Well, and finally OpenStack - the management interface program allows you to implement certain management capabilities.
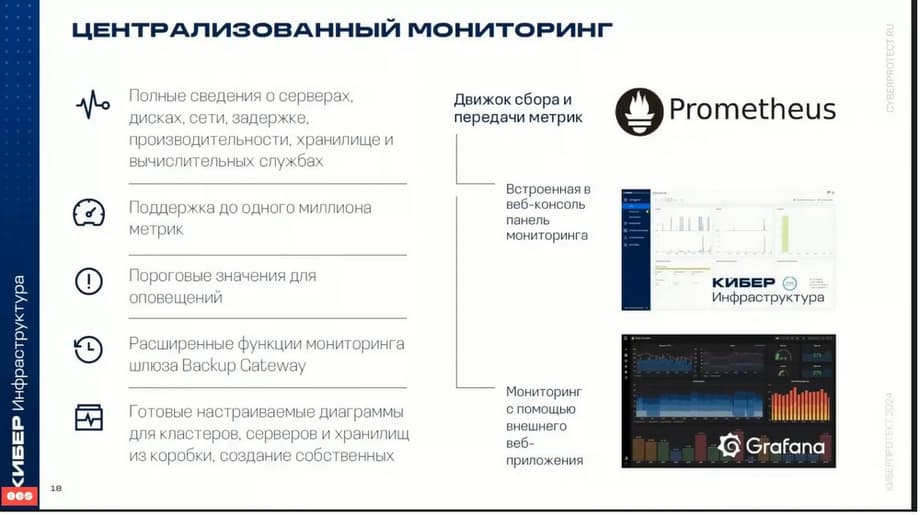
The monitoring system is used to track the health of the infrastructure and its components. It includes automated collection of metrics from all components of the system: servers, disks, networks, storage, computing services, etc. Cyberinfrastructure allows you to view all information about servers, disks, networks, latencies, performance, and manage threshold values for alerts.
The Prometheus monitoring system is also used by the cyberinfrastructure. And also, using the external web application Grafana, you can view detailed diagrams for clusters, servers, storage. And it is possible to create your own dashboards and diagrams.
Recommended hardware requirements. Here are the minimum requirements and recommended ones.
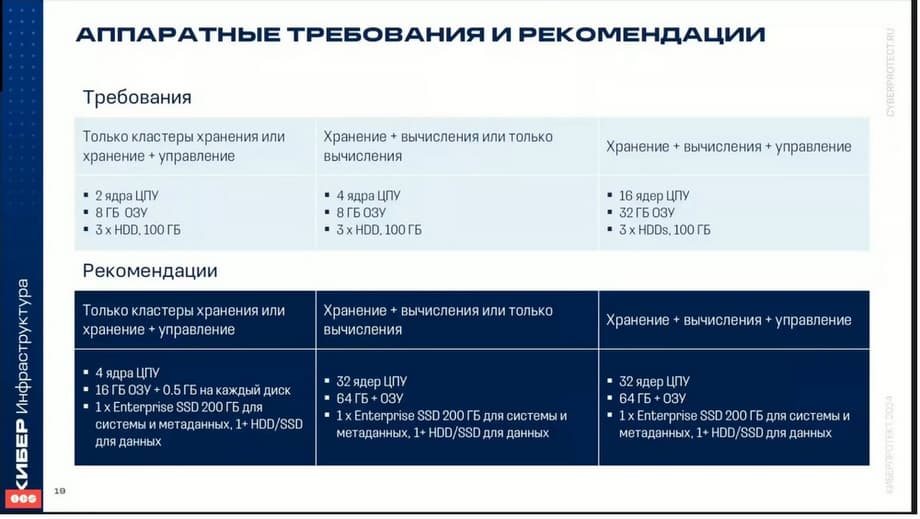
It must be said that in order to choose which servers to use, it is necessary to carry out some sizing. In order to assess the sizing, you need to understand whether this cluster will only have storage or whether it will simultaneously have both storage and computing infrastructure, i.e. virtualization will be raised. In order to determine, for example, how many CPUs and memory to take, it is also necessary to understand whether this will again be a storage thing or virtualization. If it is virtualization, then you need to estimate some maximum amount of virtual processors that is needed for virtualization, and the maximum amount of memory. For storage, it is necessary to understand what types of data storage will be used, i.e. what services will work. Each service requires some of its own parameters.

Licensing. Storage is licensed by terabytes, and it is the usable space that is licensed. As for virtualization, it is licensed by the number of server sockets. It should be said that in order to deploy in a test environment, a free license for 1 TB is included, it is included in the trial version.
Illustrations are provided by the company "Kiberprotekt".
Now on home