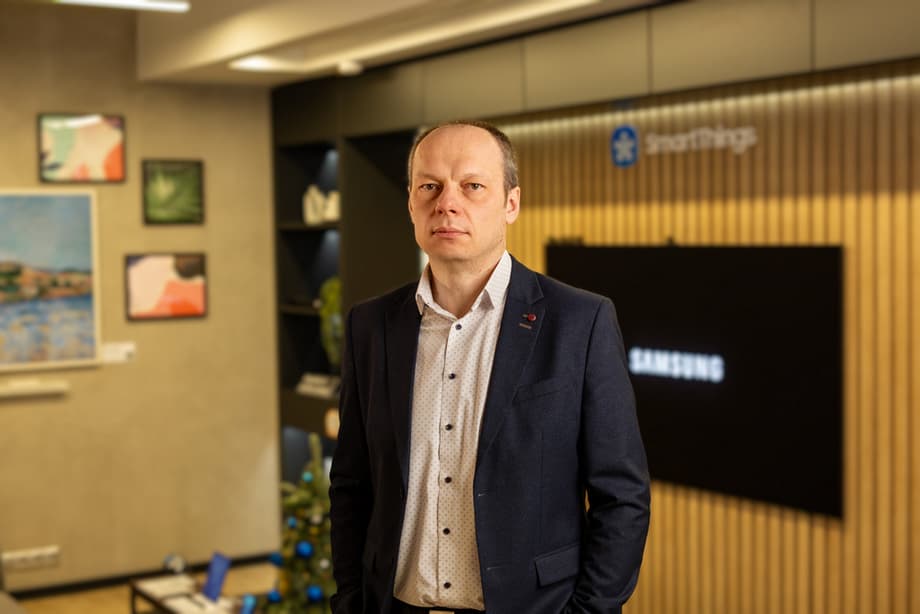
Anton Sukovaty, Director of the Service and Customer Support Division of Samsung Electronics in Russia, answers questions from the IXBT.pro editorial team

What is the key difference between original Samsung parts and non-original counterparts from a technical point of view? Which components are most often counterfeited?
Let's start with an example for smartphones. There are three main types of spare parts that are most often found in non-original versions. Battery packs lead this list. The market offers both fakes of original batteries with logos and similar markings, and those compatible in external form factor, cables and connectors, but without logos, with completely different names, etc. They are united by one thing – the difference between the stated capacity and the original. The difference in battery capacity can be 5-10%, and in some cases reaches 50%. Many such batteries are offered on marketplaces, and there are usually many negative reviews.
Another component that is most often counterfeited is the display. Here there can be both "re-glued" original matrixes onto non-original glass, and completely non-original assemblies from a matrix of a different type (for example, LCD instead of AMOLED), glass and "touchscreen". Such assemblies often have completely different characteristics: color rendering, speed, thickness, glass quality, etc.
And the "hit parade" of frequently counterfeited spare parts is completed by the back cover. In this case, the main inconsistencies are manifested in color, marking, sometimes various sensors are missing, and geometry suffers. As a result of replacing with such a cover, the mobile device loses its tightness and moisture protection.
How do Samsung parts ensure the long-term reliability of the device? What tests and checks do they undergo before installation?
Original service parts are manufactured on the same assembly lines as components for assembling finished products, including quality control.
As for reliability testing methods, there are many of them. Here is an example: the screen of the latest triple folding phone was subjected to 200,000 folding cycles in tests. Of course, each manufactured or replaced screen is not subjected to such loads before installation, but a special automated output control is mandatory.
Why can self-repair or contacting unauthorized services lead to irreversible consequences for Samsung equipment?
Let's go back to the example with a mobile phone. Indeed, with a minimum set of tools at hand, you can disassemble and assemble a phone to replace the battery or screen. But the risks of damage to the battery, back cover and other elements increase many times over with the manual method. An authorized service center uses a special machine for this. In addition, when assembling the device, it is possible to achieve tightness and check it only using the manufacturer's technology. And this requires both special consumables for gluing, and tools and devices for assembly.
Why might the device firmware work incorrectly after installing non-original parts? How does this manifest itself?
Samsung software does not impose any special restrictions on non-original spare parts. However, some parameters of the spare parts themselves may "lag behind" the original: for example, the sensitivity and speed of the touch screen, the brightness and contrast of the display, etc.
How does an official service center guarantee that the device will retain all functions after repair, including biometric authentication (fingerprint scanner)?
To do this, each device in the ASC undergoes automated output control, configuration and calibration. The very fact of conducting input and output control is recorded automatically.
Why is it important that the repair be carried out by specialists with Samsung certification? What skills and equipment are needed for the job?
The presence of a valid certificate from an ASC employee indicates that he is familiar with the current model range of the company, knows the features of assembly/disassembly, diagnostics and repair. In order to obtain certification for repairing Samsung products, ASC employees regularly undergo training courses and training.
What would you advise a user who is hesitant between a cheaper repair in an unofficial service and contacting an authorized service center?
First of all, I would like to note that repair at an official service center is not always more expensive. At least you need to compare the final price, and not advertising "from 500 rubles". And after that, I would advise you to think about the reasons and weigh the factors that are important to you as a client. How can you get a service cheaper? I don't think the real cost of the work will be very different. The cost of rent may differ depending on the location and area, but this is not the main factor in the final cost. But it is much more interesting for an unauthorized service to save on spare parts. Risking quality or choosing the original (spare part + technology) – the choice always remains with the client.
What innovations or new approaches have appeared in the work of the ASC in recent years?
In the last three years, a new type of screen repair has been actively developing - frameless. Instead of replacing the display entirely, the ASC can replace the screen or frame separately, which reduces the cost of repair for the client. Frameless repair is carried out on Samsung smartphone models of the A, F, S series.
Does Samsung or the ASC provide any forms of remote diagnostics or consultations that can help the user determine the problem before contacting the service?
Of course, we offer our customers service support in a format convenient for the customer. This includes online support through our website, messengers, social networks and chat bot. For example, the operator of the Unified Support Service, at the request of the client, can conduct remote diagnostics of the device and help solve the problem. This happens only with the consent of the client and authorization of each such session directly by the client himself.
How do Samsung and ASCs solve the issue of disposing of faulty or old devices?
A number of our service centers have special containers installed – eco-boxes. They are designed to collect portable devices that have reached the end of their service life. We regularly collect the contents of these containers and transfer them to specialized organizations for disposal.
What are Samsung's plans to expand or optimize the ASC network to ensure better service accessibility for users?
In order to increase accessibility, as mentioned earlier, Samsung is actively developing digital and hybrid communication channels. In addition, Samsung actively supports the inclusiveness of its services. One of the latest examples is the video call interface, which allows online consultations in Russian Sign Language for customers with hearing impairments. During video calls, native Russian Sign Language speakers, with the support of volunteer operators and technical specialists, advise users on the selection, purchase and maintenance of equipment. This helps to make the company's services accessible to a wider audience.